In this article, we are going to see an overview of the Threat intelligence domain in the cyber world. We are going to learn about What is Threat Intelligence, A Basic look at the Threat Intelligence Lifecycle.
What is Threat Intelligence?
“Cyber threat intelligence is information about threats and threat actors that helps mitigate harmful events in cyberspace.[1] Cyber threat intelligence sources include open-source intelligence, social media intelligence, human intelligence, technical intelligence, or intelligence from the deep and dark web.” –Wikipedia
In simpler terms, it is information collected by the organization to understand the threats that are currently targeting them or will target them in the future. This information helps the organization to build a better defense against the risk or to mitigate the risk.
This information provides information on many sophisticated vulnerabilities like Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), or global malware campaigns, and zero-day vulnerabilities. Where zero-day vulnerabilities are impossible to detect, this information can help the company or organization to protect itself better.
From the above information, you can understand why this domain is important.
Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
The Basic work in this domain is to collect the raw data and transform it into intelligence that can actually be used. The Lifecycle can depend on the organization. Here we are going to talk about the steps in the lifecycle with some basic information.
So, this lifecycle consists of 6 steps.
1. Planning/Direction/Requirement
This step can be known as planning or the direction or the Requirement step.
This is one of the most important steps in this domain. In this step, the team will plan and agree on the methodology and goals of the intel.
Some things that are decided in this step is:
- Who the attacker are and what is the motivation.
- The attack surface.
2. Collection
In this step, the team sets out to collect the raw information to satisfy the requirements set in the first step. Depending on the goals in the first step the team will usually search the open web, dark web, and other Indicators of Compromise(IoCs) To collect the information.
That’s why this phase is called the collection phase Because the raw information is collected in this phase.
3. Processing
After the raw data is collected, the information needs to be processed correctly to be analyzed. Without the proper processing, the analyst cannot analyze the data.
This phase generally consists of decrypting files, organizing the data points into spreadsheets, Translating from a foreign source, and evaluating the data relevance and reliability.
4. Analysis
Now, the raw data set has been processed. In this step, the team will perform a thorough analysis of the data set to find the potential vulnerability or issues and inform the relevant teams to solve the issues.
Basically, The team performs the analysis to answer all those questions which are asked in the requirement or the planning phase.
5. Dissemination
The information which has been generated in the previous steps has to be distributed to the intended consumers or stakeholders. Therefore, In this step, the team makes the above information presentable and digestible to the stakeholders.
6. Feedback
This is the final stage of the lifecycle. In this phase, the feedback has been provided to the report generated in the previous step. The feedback is generally provided by whoever made the initial request. This phase also checks if there is any problem or changes that need to be done in the report according to the client.
So, that’s the overview of what the lifecycle is.
Types of Threat Intelligence
There are three types of threat intelligence,
- Tactical
- Operational
- Strategic
Each of these types is one vast topic in this domain and cannot be explained in one blog. Here we will give a basic overview of these types.
Tactical
“Technical intelligence (including Indicators of Compromise such as IP addresses, file names, or hashes) can be used to assist in the identification of threat actors” –Wikipedia
Basically, It has an outline of tactics and techniques, usually, it is for a more technical audience.
Operational
“details of the motivation or capabilities of threat actors, including their tools, techniques, and procedures” –Wikipedia
Basically, it has technical details about specific attacks and campaigns.
Strategic
” intelligence about the overarching risks associated with cyber threats which can be used to drive high-level organizational strategy” — Wikipedia
Basically, it has broader or high-level trends which are usually meant for non-technical audiences.
There is a very good example by Crowdstrike to understand these steps easily.
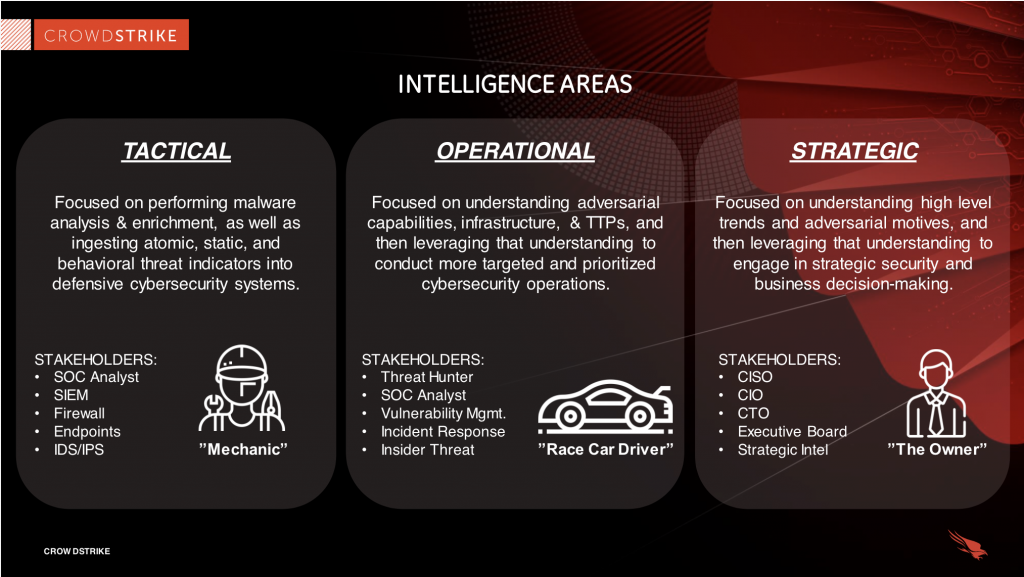
We are going to discuss all of these steps in detail in further blogs.
Below Down, there are links for further reading and tools related to this domain, Check them all to get a more clear understanding of the topic.
Resources
- A curated list of Awesome Threat Intelligence resources
// https://github.com/hslatman/awesome-threat-intelligence - A curated list of awesome threat detection and hunting resources
// https://github.com/0x4D31/awesome-threat-detection - Get the latest technical details on significant advanced malware activity
// https://www.fireeye.com/current-threats.html - 10 of the Best Open Source Threat Intelligence Feeds
// https://d3security.com/blog/10-of-the-best-open-source-threat-intelligence-feeds/ - Weekly Threat Briefing—Cyber Threat Intelligence Delivered to You
// Anomali Weekly Threat Briefing - 11 Cyber Threat Intelligence Tips
// https://www.isaca.org/resources/news-and-trends/isaca-now-blog/2016/11-cyber-threat-intelligence-tips - Threat Intelligence Defined and Explored
// https://www.forcepoint.com/cyber-edu/threat-intelligence - Cyber Threat Intelligence Feeds
// http://thecyberthreat.com/cyber-threat-intelligence-feeds/
Refrences
https://www.forcepoint.com/cyber-edu/threat-intelligence
https://www.recordedfuture.com/threat-intelligence/
https://www.crowdstrike.com/cybersecurity-101/threat-intelligence/







